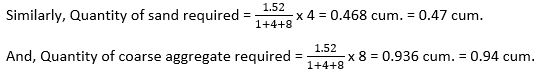- In order to calculate the quantities of materials required for brick work in cement mortar, it is necessary to decide the size of the bricks to be used in the masonry.
- The size of the conventional or traditional bricks vary from 8 3/4″ x 3 3/16″ x 2 5/8″ (i.e. 22.23 cm x 10.64 cm x 6.67 cm) to 9″ x 4 1/2″ x 3″ (i.e. 22.86 cm x 11.43 cm x 7.62 cm)
- The new I.S. size brick i.e. modular brick is actual 19 cm x 9 cm x 9 cm with a frog of 10 cm x 4 cm x 1 cm size.
- Normally, the mortar joint is taken as 1 cm throughout, therefore, the normal size of brick will be 20 cm x 10 cm x 10 cm.
Therefore, Volume of one I.S. size brick, with thickness of joint as 1 cm = 0.20 x 0.1 x 0.1 = 0.002 cum.
Therefore, For 1 cum. of brick work, the total number of I.S. size (i.e. modular) bricks required = 1 cum. /0.002 = 500 Nos.
Therefore, Adding 5% towards wastage = 25
Therefore, Total number of I.S. bricks required = 525 Nos.
Now,
Quantity or volume of wet mortar required = (Total volume of brick work) – (Volume occupied by 500 bricks of 19 cm x 9 cm x 9 cm size)
= (1 – 500 x 0.19 x 0.09 x 0.09) cum
= 1 – 0.7695
=0.2305 cum.
In order to allow for mortar for filling the frog, bonding and wastage during its use, 10% is to be added.
Therefore, Volume of wet mortar required = 0.2305 + 0.10 x 0.2305
= 0.235 cum.
Therefore, Dry volume of mortar required = 1.25 x 0.235
= 0.316 = 0.30
i.e. Approximately for 1 cum. of brick work, 30% of the dry mortar will be required.
Calculations of materials for 1 cum. of brick work in C.M. (1:6) with traditional size bricks 9″ x 4.375″ x 2.75″ (i.e. 22.86 cm x 11.11 cm x 6.985 cm)
Assuming thickness of joint as 1 cm throughout, the nominal size of traditional bricks = 23.86 cm x 12.11 cm x 7.985 cm
Therefore, Volume of one traditional size brick with 1 cm as thickness of joint = (0.2386 x 0.1211 x 0.07985) cum. = 0.002307 cum.
Number of traditional bricks required for 1 cum. of brickwork = 1/0.002307
= 433 Nos.
Add 5% towards wastage = 22
Therefore, Total number of traditional bricks required = 455 Nos.
Now, Value of wet mortar required = 1 – 433 x (0.2286 x 0.1111 x 0.06985)
= 1 – 0.77
= 0.23 cum. which is practically same as derived above
Therefore, Adding 10% extra for wastage = 0.023 cum.
Therefore, Wet volume of mortar required = 0.253 cum.
Therefore, Dry volume required = 1.25 (wet volume)
= 1.25 x 0.253
=0.316 cum. = 0.30 cum.
i.e. approximately 30% of dry volume of mortar is required for constructing 1 cum. of brick work. Further, knowing the proportion of cement mortar the quantities of cement (in bags) and sand can be worked out as usual.
e.g. knowing the proportion of the cement mortar, the quantities of cement and sand required can be determined as follows.
For cement mortar (1:6) proportion,
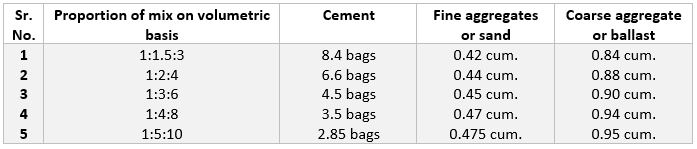
Quantity of cement required = (Dry volume of mortar)/(1+6) = (0.316/7)
= 0.045 cum. = 0.045 x 30 = 1.35 bags of cement
and, Quantity of sand required = (0.316/7) x 6 = 0.2708 cum. = 0.27 cum.
Approximate method:
The above quantities can be determined by an approximate method as follows:
For 1 cum. of brick work divide 0.3 by the sum of the proportion of the material to obtain the quantity of cement in cubic metre
i.e. Quantity of cement required = (0.3)/(1+6) = 0.3/7 = 0.043 cum.
But as certain amount of cement will be required to fill the voids in the sand, add 0.002 cubic metre extra.
Therefore, Quantity of cement required = 0.043 + 0.002 = 0.045 cum. which is same as above
Therefore, Number of cement bags required = 0.045 x 30 = 11.35 bag
and, Quantity of sand required = 0.045 x 6 = 0.27 cum.